Introduction
A brick is a smallest building unit or a small rectangular block typically made of fired or sun-dried clay used in construction. Clay bricks are commonly used since these are economical and easily available.
Specification for common burnt clay building bricks- IS-1077 (reaffirmed – 2021).
Specification for heavy duty burnt clay building bricks- IS-2180 (reaffirmed- 2021).
Size of brick
- Standard size- 19cm x 9cm x 9cm (length x breadth x height respectively).
- Nominal size / size of brick along with mortar- 20cm x 10cm x 10cm (length x breadth x height respectively).
- Conventional size of brick- 22.4cm x 11.4cm x 7.6cm (length x breadth x height respectively).
- Country bricks or field bricks- 9” x 4.5” x 3”.
Classification of Bricks
On the basis of field practice:-
- First class bricks:- These bricks have standard shapes, sharp edges and smooth surface because they are molded into table-molding and burnt in large kilns. They have more durability and strength and are used in permanent structures.
- Second class bricks:- These are ground-molded and therefore, do not have smooth surfaces and sharp edges. Shapes are also irregular due to unevenness in ground. These bricks will also give the best strength and durability. Smooth plastering required on the brick structure.
- Third class bricks:- They are ground-molded and clamp burnt bricks, hence, are of poor quality. They are generally used for temporary structures like unburnt bricks. Surfaces are rough and have unfair edges.
- Fourth class bricks:- They are very quality bricks, as they are obtained by overburning. They are not suitable for construction purposes. They are used as aggregates in the manufacturing of concrete.

On the basis of strength:-
Class 3.5-35 MPa.
On the basis of use:-
- Common bricks
- Facing bricks
- Engineering bricks
On the basis of types:-
- Solid bricks

- Perforated bricks

- Hollow bricks

- Cellular bricks
Composition of bricks
- Silica- 50-60%
- Alumina- 20-30%
- Lime – 4-5%
- Oxide of iron- 5-6%
- Magnesia- 1%
Different forms of bricks
- Round ended brick:- Used to construct open drains.

- Bullnose brick- Used to construct open drains.

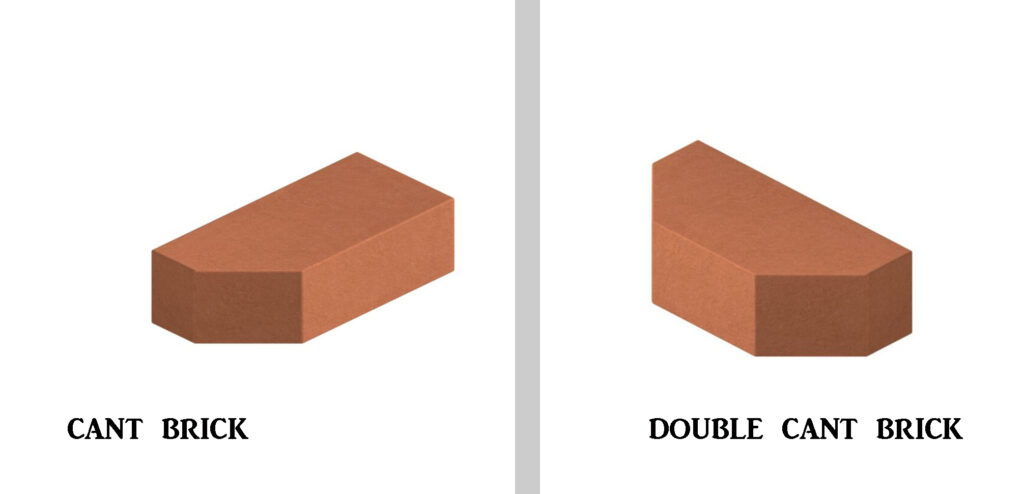
- Cant brick and double cant brick- Used for door and window jambs.
- Cornice brick.

- Compass brick- Tapered along length
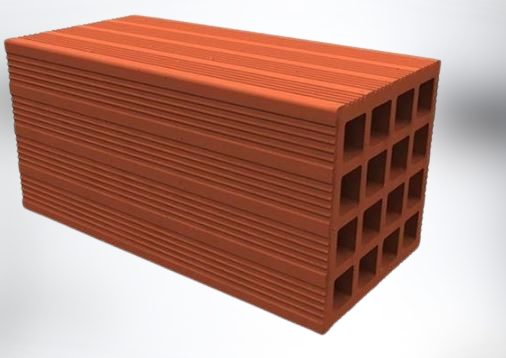
6. Perforated brick

- Hollow brick.
- Coping brick- used on parapet walls.

Brick masonry
- Stretcher- Longer side face of the brick.
- Header- shorter side face of the brick and used for hearting of walls.
- Closures- The portion of the brick cut along the length.
- Queen closure (half).
- Queen closure (quarter).
- King closure ( one length and one width- same ; one length and one width – half).
- Bevelled closure (one length and one width- same ; one length is removed and one width is halved)
- Mitered closure (one length and one width are same ; one length is halved and one width is removed).
4. Bats- the portion of the bricks cut along its width.
a.Half bat
b.Three-quarter bat
c. Bevelled bat
5.Quoin- The term, in French, stands for “corner”. It is the external angle at the face of the wall that is greater than equal to 90 degree.
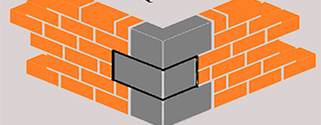
Bonding in brick masonry
- English bond
- Flemish bond
- Stretcher bond
- Header bonds

